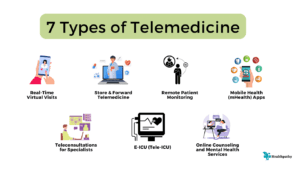
7 Types of Telemedicine
Telemedicine, a revolution in the healthcare industry, leverages technology to provide remote medical services, bridging the gap between patients and healthcare providers. With the advent of high-speed internet and advancements in communication technologies, telemedicine has witnessed rapid growth, transforming the way medical care is delivered. In this article, we will delve into seven distinct types of telemedicine applications, each catering to specific medical needs and enhancing patient access to quality healthcare.
1. Real-Time Virtual Visits:
Real-time virtual visits represent one of the most prevalent forms of telemedicine. This type involves live video or audio consultations between patients and healthcare providers. Through secure platforms, patients can interact with doctors, discuss symptoms, seek advice, and receive treatment recommendations, all from the comfort of their homes. Real-time virtual visits are particularly beneficial for non-emergency medical issues, follow-up appointments, and routine check-ups. They reduce the need for physical visits and offer convenience to patients, especially those in rural or remote areas.
2. Store-and-Forward Telemedicine:
Store-and-forward telemedicine employs the transmission of medical data, such as images, videos, and patient information, from one healthcare provider to another. Unlike real-time virtual visits, there is no live interaction between patients and doctors. Instead, specialists review the data at a later time and provide their expert opinion. This type of telemedicine is advantageous in fields like radiology, dermatology, and pathology. Store-and-forward telemedicine improves the efficiency of consultations, reduces waiting times, and allows for better utilization of specialized expertise.
3. Remote Patient Monitoring:
Remote patient monitoring involves the use of technology to collect and transmit patients’ health data from remote locations to healthcare providers. Patients wear devices or sensors that measure vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, glucose levels, or activity levels. The data is then securely transmitted to healthcare professionals who can remotely monitor patients’ conditions. This form of telemedicine is particularly useful for managing chronic diseases, post-surgery recovery, and keeping a close eye on high-risk patients. It empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare management and enables early intervention in case of any anomalies.
4. Mobile Health (mHealth) Apps:
Mobile Health or mHealth apps are smartphone applications designed to offer a range of healthcare services, information, and self-assessment tools to users. These apps cover diverse areas, such as fitness tracking, mental health support, medication reminders, and general health information. Patients can access personalized health data, receive health tips, and manage their well-being with ease. Moreover, mHealth apps facilitate secure communication between patients and healthcare providers, enabling virtual consultations and remote monitoring.
5. Teleconsultations for Specialists:
Teleconsultations for specialists enable patients and primary care physicians in underserved or remote regions to consult with specialized medical professionals located in larger healthcare centers. Through video conferencing and telecommunication tools, patients can seek expert opinions, receive complex diagnoses, and discuss treatment plans without the need to travel long distances. This type of telemedicine significantly improves access to specialized care, ensuring patients receive the best possible medical attention regardless of their geographical location.
6. E-ICU (Tele-ICU):
E-ICU, also known as Tele-ICU, extends critical care expertise to remote locations or smaller hospitals lacking round-the-clock access to intensive care specialists. Through a network of cameras, sensors, and real-time data transmission, remote healthcare teams can closely monitor patients in intensive care units. This allows them to promptly intervene and provide timely care, reducing the risks associated with critical medical conditions. E-ICU systems have demonstrated positive outcomes, including decreased mortality rates and improved patient outcomes.
7. Online Counseling and Mental Health Services:
Telemedicine has been instrumental in addressing mental health needs, especially during challenging times. Online counseling platforms and mental health apps provide access to licensed therapists and mental health professionals through video calls, voice calls, or secure messaging. Patients can receive therapy sessions, counseling, and emotional support from the privacy of their homes. Telemedicine in mental health care significantly reduces the stigma surrounding mental health and enhances access to mental health services.
Summary:
Telemedicine has revolutionized healthcare delivery, providing innovative solutions to enhance patient access to medical services while ensuring convenience and efficiency. As technology continues to advance, telemedicine will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare, improving patient outcomes, and creating a more connected and inclusive healthcare ecosystem.
Related Articles:


Follow us: