Heart Disease Risk Calculator
Cardiovascular diseases, particularly heart attacks, are a leading cause of death worldwide. To address this critical health issue, healthcare professionals have developed various risk assessment tools, including heart disease risk calculators. These calculators are essential in evaluating an individual’s risk of experiencing a heart disease over a specific period, allowing for timely preventive measures and lifestyle modifications. This article aims to explain the significance of heart disease risk calculators, their key components, and how they empower individuals and healthcare providers in combating heart disease.
Understanding Heart Disease Risk Factors
Before delving into the specifics of heart attack risk calculators, it is crucial to understand the risk factors associated with cardiovascular diseases. These risk factors can be categorized as modifiable and non-modifiable. Modifiable risk factors include smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary habits, obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels. Non-modifiable risk factors include age, gender, family history of heart disease, and genetic predisposition.
Importance of Heart Disease Risk Calculators
Heart attack risk calculators provide a systematic and evidence-based approach to assessing an individual’s likelihood of experiencing a heart attack. By evaluating both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, these calculators help identify high-risk individuals who may benefit from preventive interventions. Early detection of high-risk individuals enables healthcare providers to intervene with personalized treatment plans, lifestyle changes, and medication to reduce the risk of heart attacks.
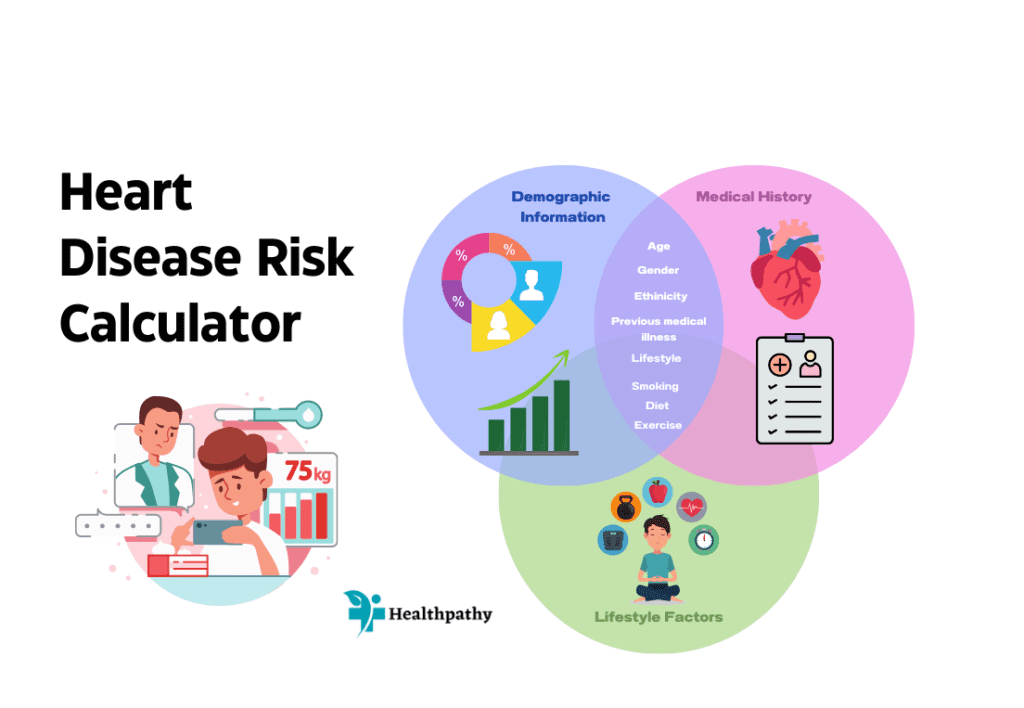
Key Components of Heart Disease Risk Calculators
- Demographic Information: Heart disease risk calculators typically require basic demographic information, such as age, gender, and ethnicity. These factors help determine the baseline risk of heart disease.
- Medical History: Individuals are asked about their medical history, including any previous cardiovascular events, diabetes, hypertension, and cholesterol levels. A family history of heart disease is also considered.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, like smoking, physical activity level, and dietary habits, play a significant role in heart disease risk. Heart attack risk calculators incorporate these factors to assess an individual’s overall risk.
- Physical Measurements: Some risk calculators may require physical measurements like blood pressure, body mass index (BMI), and cholesterol levels to refine risk assessments further.
- Timeframe: Heart attack risk calculators estimate the risk over a specific timeframe, often ten years. This timeframe aids in both short-term and long-term risk assessment and enables timely intervention.
Types of Heart Disease Risk Calculators
Several well-known heart disease risk calculators exist, with variations based on geographical location and population demographics. Notable examples include:
a. Framingham Risk Score: One of the earliest risk calculators, the Framingham Risk Score, considers age, gender, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, blood pressure, and smoking status.
b. Reynolds Risk Score: This calculator adds C-reactive protein (CRP) and family history to the factors included in the Framingham Risk Score.
c. ACC/AHA Pooled Cohort Equations: Developed by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA), this calculator assesses atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk, including heart attacks, over ten years.
Benefits and Limitations of Heart Disease Risk Calculators
Benefits:
- Enable personalized risk assessment based on individual characteristics.
- Encourage lifestyle modifications for those at high risk, reducing the overall burden of heart disease.
- Help healthcare providers identify candidates for preventive treatments and interventions.
- Increase awareness about cardiovascular health and heart attack risks.
Limitations:
- Not all risk calculators are equally accurate for every population group.
- May not account for all possible risk factors.
- Cannot predict heart attacks with certainty, but estimate risk over a period.
- Reliance on self-reported data may introduce errors.
Conclusion
Heart disease risk calculators are indispensable tools in the fight against cardiovascular diseases, providing valuable insights into individual risk profiles. These calculators consider a range of modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors to estimate the likelihood of a heart attack over a specified period. By identifying high-risk individuals, healthcare providers can implement targeted interventions and lifestyle modifications, potentially preventing heart attacks and improving overall cardiovascular health. Nevertheless, it is essential to recognize that risk calculators serve as aids, not definitive predictions, and should complement professional medical advice and regular health check-ups. Empowering individuals with knowledge about their heart health can lead to a healthier society and a reduced burden of heart disease.
More To Read:

Follow us:





