Physical Determinants of Health
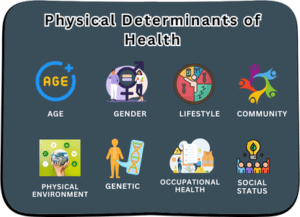
Health is a multi-faceted concept influenced by a myriad of factors. While genetics and personal behaviors are often at the forefront of discussions about health, the role of physical determinants should not be overlooked. These determinants encompass a wide range of elements that contribute to our overall well-being, from our genetic makeup to the environments in which we live and work. Understanding the intricate interplay of these physical determinants is essential for crafting effective public health policies, personalized healthcare interventions, and individual wellness strategies.
Genetics and Health:
Our genetic code acts as the blueprint for our bodies, influencing not only our physical characteristics but also our health vulnerabilities. Genetic predisposition can significantly impact our susceptibility to various diseases and conditions. For instance, certain genetic markers can heighten the risk of heart disease, diabetes, or specific types of cancer. The emergence of genetic testing has revolutionized healthcare by allowing for personalized medicine. These tests provide insights into an individual’s genetic profile, enabling healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans and preventive measures accordingly. As our understanding of genetics continues to deepen, the potential for more precise and effective healthcare interventions becomes increasingly apparent.
Age and Health:
Aging is a natural and inevitable part of life, accompanied by a series of physiological changes that can impact health. As individuals age, their bodies undergo transformations that affect various bodily systems. Age-related health conditions such as osteoporosis, cognitive decline, and diminished immune function become more prevalent. However, embracing a proactive approach to healthy aging can mitigate these effects. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, and mental stimulation are among the strategies that promote optimal well-being in later years. By adopting a comprehensive approach to aging, individuals can maintain their quality of life and independence.
Gender and Health:
Biological differences between genders result in distinct health experiences. Hormonal variations contribute to differences in disease susceptibility, symptom manifestation, and treatment responses. For instance, cardiovascular disease may present differently in men and women, and gender-specific healthcare considerations are crucial for ensuring equitable and effective treatment. Addressing gender-related health disparities requires an understanding of the biological nuances as well as the social and cultural factors that contribute to differential health outcomes. By tailoring medical care and public health initiatives to accommodate these differences, we can strive for gender-sensitive healthcare that addresses the unique needs of all individuals.
Physical Environment and Health:
The environments in which we live, work, and play have a profound impact on our health. Air and water quality are fundamental determinants of respiratory and gastrointestinal health. Exposure to pollutants and toxins can lead to various health issues, ranging from respiratory diseases to long-term chronic conditions. Urban planning and community design also play a crucial role in shaping health outcomes. Walkable neighborhoods, access to green spaces, and proximity to healthcare facilities contribute to healthier lifestyles. By prioritizing clean air, water, and sustainable urban development, communities can create environments that promote physical well-being and mental health.
Occupational Health:
The workplace is a setting where physical determinants of health are particularly evident. Occupational hazards and exposure to harmful substances can result in immediate injuries or chronic health issues over time. Additionally, work-related stress is a significant contributor to mental health problems. Creating safe and supportive work environments is paramount for maintaining employee well-being and productivity. Implementing measures such as proper safety protocols, ergonomics, and work-life balance initiatives can lead to improved overall health outcomes for workers.
Lifestyle and Health:
Individual lifestyle choices have a profound impact on health. Nutrition, physical activity, and sleep patterns are key factors that influence overall well-being. A balanced and nutritious diet provides the body with essential nutrients for growth, maintenance, and disease prevention. Regular physical activity is associated with reduced risks of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Adequate sleep is vital for cognitive function, mood regulation, and immune system support. Promoting healthy behaviors through education and accessible resources is crucial for empowering individuals to make informed choices that positively impact their health.
Socioeconomic Status and Health:
Socioeconomic status is a powerful determinant of health, influencing access to healthcare, education, and living conditions. Individuals with higher socioeconomic status generally have greater access to healthcare services, healthier living environments, and more resources for health-promoting activities. Conversely, those facing poverty often experience barriers to adequate healthcare, education, and nutritious food. These disparities contribute to higher rates of chronic diseases and reduced life expectancy among marginalized populations. Addressing socioeconomic inequalities requires comprehensive approaches that prioritize equitable access to resources and opportunities.
Community Design and Health:
The design of communities has a significant impact on health outcomes. Access to green spaces encourages physical activity and reduces stress, leading to improved mental and physical well-being. Well-designed urban environments that prioritize walking and cycling infrastructure promote active lifestyles and reduce reliance on motorized transportation. Furthermore, the availability of safe neighborhoods, public transportation, and community facilities enhances social interaction and fosters a sense of belonging. Community design can shape behaviors and support the creation of healthier societies.
Summary:
The intricate web of physical determinants of health underscores the complexity of achieving and maintaining optimal well-being. From genetics to environmental conditions, each determinant plays an essential role in shaping health outcomes. By recognizing and addressing these determinants through a multidisciplinary approach that spans healthcare, policy, and community development, we can work towards creating healthier societies and improving the quality of life for all individuals. As we continue to deepen our understanding of these determinants, we pave the way for a future where health is not merely the absence of disease but a state of flourishing and vitality.
Related Article:

Follow us: