Types of Telehealth

Telehealth, a revolutionary advancement in the healthcare industry, has transformed the way medical services are delivered and received. Through the use of technology, telehealth has bridged the gap between patients and healthcare providers, offering a wide array of services that cater to various healthcare needs. This article deals into the diverse types of telehealth services, highlighting their benefits, challenges, and impact on healthcare accessibility.
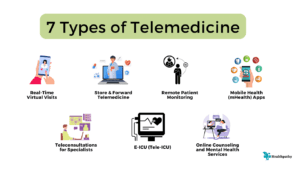
Synchronous Telehealth Services:
Synchronous telehealth services involve real-time interactions between patients and healthcare providers. Video consultations have become increasingly popular, allowing patients to communicate with doctors or specialists remotely. Patients in rural or remote areas can access healthcare expertise without the need for long-distance travel, thereby reducing costs and time constraints.
Mental health counseling has also seen significant growth through video consultations, providing convenient and confidential therapy sessions to individuals who might otherwise struggle to access such services.
Virtual visits, a subset of synchronous telehealth, gained widespread adoption during the COVID-19 pandemic. These virtual appointments became essential in maintaining non-emergency medical care while minimizing exposure risks. Though they offer convenience and accessibility, virtual visits may not be suitable for every medical condition, emphasizing the importance of striking a balance between virtual and in-person care.
Asynchronous Telehealth Services:
Asynchronous telehealth services do not require immediate real-time interactions. Store-and-forward telehealth allows medical professionals to share patient information, such as medical images and test results, with specialists for consultation. This system proves invaluable for radiology and dermatology consultations, as it enables experts to provide timely feedback without the need for patients to be physically present.
Secure messaging and email consultations facilitate ongoing communication between patients and providers. Follow-up discussions, prescription refills, and general health inquiries can be efficiently addressed through this method. Additionally, remote patient monitoring (RPM) falls under asynchronous telehealth, where patients use wearable devices to monitor vital signs or chronic conditions. RPM empowers patients to actively participate in managing their health, while healthcare providers can offer timely interventions based on the data received.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
RPM allows healthcare professionals to remotely monitor patients’ health data, such as blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate, on a continuous basis. This service is particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or hypertension. RPM enables early detection of potential health issues, leading to timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications:
The rise of mobile health applications has revolutionized healthcare accessibility. These apps empower individuals to track their health and wellness, monitor fitness goals, and manage chronic conditions efficiently. Virtual health platforms offer on-demand services, connecting patients with healthcare providers for medical consultations and guidance through smartphone or tablet applications.
Telehealth for Mental Health Support
Telehealth has been a game-changer in the realm of mental health support. Virtual therapy sessions and counseling have broken barriers, making mental health services more accessible and convenient. Online support groups and communities provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences and seek support from others facing similar challenges. Telehealth’s role in mental health has been pivotal in destigmatizing mental health issues and encouraging open conversations.
Telehealth for Rural and Underserved Areas
Telehealth has emerged as a lifeline for rural and underserved communities where access to healthcare facilities is limited. By leveraging telehealth services, these communities can access specialist care, preventive health education, and chronic disease management remotely. However, challenges like reliable internet connectivity and technology literacy need to be addressed to ensure equitable access to telehealth services.
Telehealth for Home Care and Aging Populations
Telehealth plays a vital role in providing healthcare services to homebound individuals and the elderly. Remote patient monitoring allows healthcare providers to closely monitor elderly patients, ensuring their safety and well-being. Telemedicine services enable seniors to receive medical consultations from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and enhancing their quality of life.
Telehealth in Emergency and Disaster Situations
In emergencies and natural disasters, telehealth becomes a crucial tool for providing medical assistance and triage services. Teletriage enables healthcare professionals to assess patients remotely and prioritize care based on the severity of their condition. Telehealth deployment during disasters facilitates continuity of care when traditional healthcare infrastructure may be compromised, ensuring that medical services can still reach those in need.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Telehealth
While telehealth offers numerous benefits, it also raises legal and ethical concerns that must be addressed. Regulations surrounding telehealth licensure and reimbursement vary between regions, impacting its widespread adoption. Data security and patient privacy are critical aspects that require stringent measures to protect sensitive medical information.
Future of Telehealth
The future of telehealth holds immense potential. Advancements in telehealth technology, such as virtual reality and augmented reality, may further enhance the patient-provider experience. The integration of artificial intelligence could lead to more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans. As telehealth continues to evolve, it will likely become an integral part of the healthcare ecosystem, contributing to improved healthcare outcomes and increased accessibility.
Conclusion
Telehealth has emerged as a powerful tool that revolutionizes healthcare accessibility and delivery. The various types of telehealth services, including synchronous and asynchronous solutions, remote patient monitoring, mHealth applications, mental health support, and its application in diverse settings, demonstrate its transformative impact on healthcare. While challenges persist, the potential benefits of telehealth are immense, promising a future where quality healthcare is accessible to all, regardless of location or circumstance. Embracing telehealth’s potential is a step toward building a healthier and more inclusive world.
Related Articles:

Follow us: