Health Inequity Definition
Health inequity, a pressing issue affecting societies worldwide, is the unjust and avoidable disparity in health outcomes and access to healthcare services among different populations. Unlike health disparities, which refer to variations in health outcomes, health inequities stem from systemic and structural factors that result in unequal opportunities for good health. This article delves into the definition of health inequity, its causes, and its profound implications for individuals and societies.
Health Inequity
It is rooted in social injustices and can manifest along various axes, including socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, gender, geographical location, and more. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health equity as “the absence of unfair and avoidable or remediable differences in health among population groups defined socially, economically, demographically, or geographically.”
In simpler terms, health inequity means that people who are already disadvantaged due to societal structures and historical factors face additional barriers that prevent them from achieving their optimal health. These barriers can include a lack of access to quality healthcare, education, clean water, nutritious food, safe living conditions, and economic opportunities.
Causes of Health Inequity
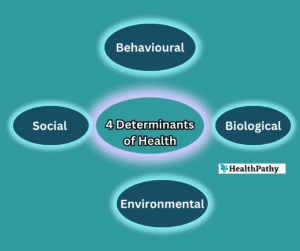
Health inequities result from a complex interplay of social, economic, political, and cultural factors. Some key contributing factors include:
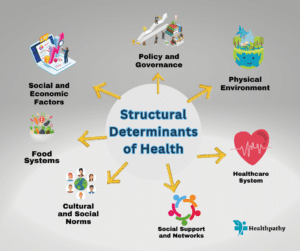
Social Determinants of Health:
Conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age significantly impact their health. Limited access to education, income inequality, housing instability, and discrimination can lead to disparities in health outcomes.
Structural Racism and Discrimination:
Racial and ethnic minorities often experience discrimination, which affects their opportunities for education, employment, and healthcare access. This, in turn, contributes to health inequities.
Healthcare Access and Quality:
Unequal access to healthcare services, including preventive care and timely treatments, can exacerbate health inequities. Disparities in the quality of care received by different populations also contribute to inequitable health outcomes.
Geographical Disparities:
People living in rural or remote areas may face challenges in accessing healthcare facilities and services, leading to health disparities.
Cultural and Language Barriers:
Cultural norms and language barriers can hinder effective communication between patients and healthcare providers, impacting health outcomes.
Implications of Health Inequity
Health inequity has far-reaching consequences that extend beyond individual well-being:
Social Injustice:
Health inequity is a manifestation of broader societal inequalities and injustices. It reinforces and perpetuates existing disparities in education, income, and social status.
Economic Burden:
Health inequities result in increased healthcare costs, lost productivity, and decreased economic growth. This burden affects not only individuals but also healthcare systems and economies as a whole.
Poor Public Health Outcomes:
Health inequities can lead to higher rates of preventable diseases, premature deaths, and reduced life expectancy in marginalized communities.
Strained Healthcare Systems:
Unequal distribution of healthcare resources can strain healthcare systems and limit their capacity to provide timely and effective care to all populations.
Social Cohesion:
Health inequities can erode social cohesion and trust within communities, as individuals from marginalized groups may perceive themselves as being neglected or discriminated against.
Addressing Health Inequity
Addressing health inequity requires concerted efforts across various levels, from policy changes to community engagement:
Policy Reform:
Governments and organizations need to implement policies that address social determinants of health, promote healthcare access, and reduce discrimination.
Healthcare Equity:
Ensuring equal access to quality healthcare services and culturally competent care is essential for reducing health inequities.
Education and Awareness:
Promoting health literacy and raising awareness about the causes and consequences of health inequities can empower individuals to advocate for change.
Research and Data Collection:
Collecting and analyzing data on health disparities can help identify specific areas that need intervention and track progress over time.
Community Engagement:
Engaging communities affected by health inequities in decision-making processes can lead to more effective and sustainable solutions.
Summary:Health Inequity Definition
Health inequity is a deeply rooted issue that reflects broader societal disparities. Understanding its definition, causes, and implications is the first step toward addressing this critical challenge. By advocating for policy changes, promoting healthcare access, and fostering social awareness, individuals, communities, and governments can work together to create a more just and equitable healthcare system where everyone has the opportunity to attain their highest level of health.
Related Articles:


Follow us: Health Inequity Definition