Social Determinants of Health

In the pursuit of better health and well-being for all individuals, it’s essential to understand that health is influenced by more than just medical care. Social determinants of health (SDOH) play a pivotal role in shaping people’s overall health outcomes. These determinants encompass a wide range of social, economic, and environmental factors that interact to affect an individual’s health status and quality of life. This article delves into the significance of social determinants of health, their key components, and their impact on societies.
What are Social Determinants?
Social determinants of health refer to the conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age. They include a complex interplay of various factors that go beyond traditional healthcare, influencing health outcomes across the lifespan. These determinants are deeply intertwined and can act as barriers or facilitators to achieving optimal health.
Key Components of Social Determinants of Health
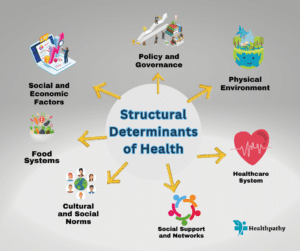
Socioeconomic Status: Economic factors, such as income, employment, and education, significantly influence health outcomes. Individuals with higher incomes and more education tend to have better access to healthcare, nutrition, and safer living conditions.
Neighborhood and Physical Environment: The environment in which people live can impact their health. Access to clean air and water, green spaces, safe housing, and infrastructure all play a role in health outcomes.
Healthcare Access and Quality: Access to healthcare services and the quality of care received are critical components. Unequal access and health disparities in healthcare can lead to poor health outcomes.
Social Support Networks: Strong social networks and support systems can positively affect mental health and physical well-being. Isolation and lack of social support can lead to negative health impacts.
Cultural and Social Norms: Cultural practices and societal norms influence health behaviors and decisions. Understanding cultural factors is essential for providing effective healthcare.
Education and Literacy: Higher levels of education and health literacy are linked to better health outcomes. Education equips individuals with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their health.
Employment and Working Conditions: Job security, workplace safety, and job-related stress can impact both physical and mental health.
Impact of Social Determinants of Health
The influence of social determinants of health is profound and wide-reaching:
Health Disparities: Disparities in social determinants often lead to health inequities. Marginalized populations are more likely to face challenges in accessing quality healthcare, nutritious food, and safe living conditions.
Disease Risk: Social determinants play a role in the development of chronic diseases. For instance, individuals with limited access to fresh produce are at higher risk of obesity and related conditions.
Maternal and Child Health: SDOH influences maternal and child health outcomes. Lack of access to prenatal care, adequate nutrition, and safe environments can impact infant mortality rates.
Mental Health: Economic instability, social isolation, and adverse living conditions can contribute to mental health issues.
Healthcare Utilization: Individuals facing socioeconomic challenges may delay seeking medical care due to financial constraints, leading to more advanced disease stages.
Longevity: Social determinants directly impact life expectancy. People with favorable determinants tend to live longer, healthier lives.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health
Addressing social determinants of health requires a multi-pronged approach:
Policy Changes: Governments and organizations can implement policies that promote education, affordable housing, fair wages, and access to nutritious food.
Community Engagement: Involving communities in decision-making processes can lead to solutions that address local needs and challenges.
Healthcare Access: Efforts should be made to ensure that all individuals, regardless of their background, have equal access to quality healthcare services.
Education and Empowerment: Promoting education and health literacy empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Cross-Sector Collaboration: Collaboration between healthcare, education, housing, and employment sectors can lead to comprehensive solutions.
Summary:
Social determinants of health are the underlying factors that shape an individual’s health trajectory. Acknowledging and addressing these determinants are essential for achieving health equity and ensuring that everyone has an equal opportunity to attain their highest level of health. By recognizing the complex interplay of social, economic, and environmental factors, societies can work towards creating a healthier and more equitable future for all.
Related Articles:

Follow us:





