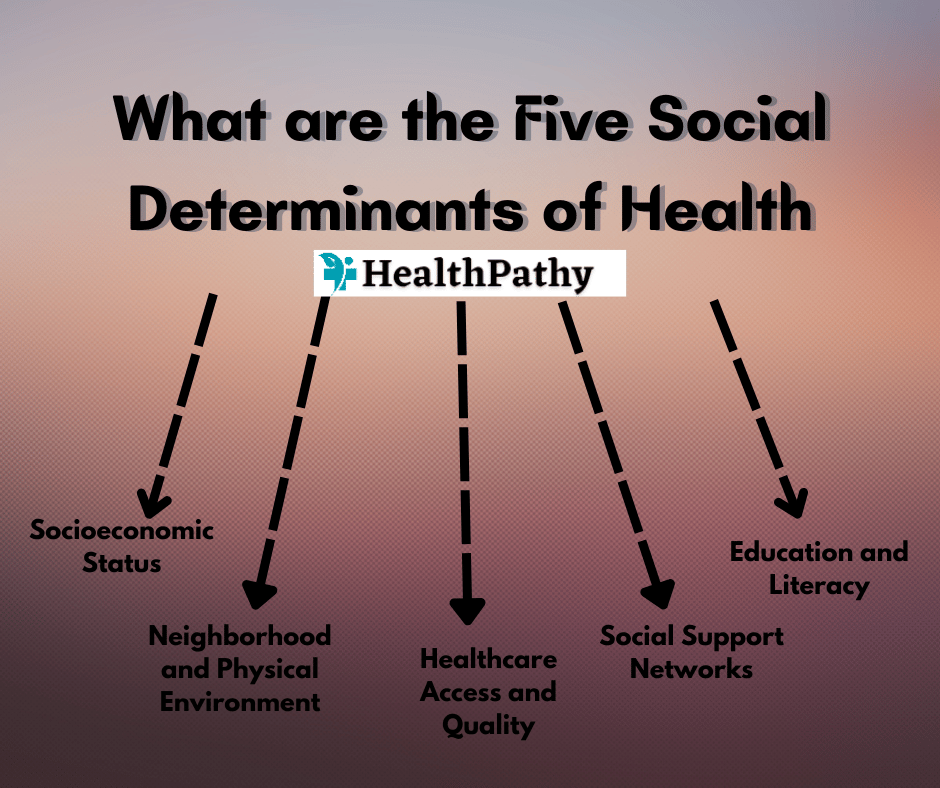
What are the Five Social Determinants of Health

Understanding health goes beyond medical care; it encompasses a complex web of interconnected factors that collectively determine an individual’s well-being. Social determinants of health (SDOH) are fundamental components that significantly shape an individual’s health outcomes and overall quality of life. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the five key social determinants of health, highlighting their significance, impact, and the ways they intersect.
Socioeconomic Status (SES)
Socioeconomic status refers to an individual’s social and economic position within a society, often characterized by factors such as income, education, occupation, and wealth.
Significance:
Socioeconomic status is a cornerstone determinant that influences health outcomes across various domains.
Impact:
- Access to Resources: Higher SES individuals have better access to healthcare, nutritious food, safe living conditions, and educational opportunities.
- Healthcare Utilization: Those with higher SES are more likely to seek preventive care, early disease detection, and timely medical interventions.
- Health Behaviors: Higher SES is associated with healthier lifestyle choices, such as balanced diets, exercise, and reduced tobacco/alcohol use.
Neighborhood and Physical Environment
The neighborhood and physical environment encompass the geographical area in which individuals live, including its characteristics, resources, and built environment.
Significance:
The surroundings in which people live profoundly influence their health and well-being.
Impact:
- Exposure to Environmental Hazards: Poor air and water quality, lack of green spaces, and unsafe housing can lead to various health issues.
- Community Infrastructure: Access to healthcare facilities, grocery stores, and recreational areas affects an individual’s overall quality of life.
- Safety and Crime Rates: High crime rates and unsafe neighborhoods can lead to stress and negatively impact mental health.
Healthcare Access and Quality
Healthcare access and quality pertain to an individual’s ability to obtain timely and appropriate medical care when needed.
Significance:
Access to healthcare services and receiving quality care are crucial for preventing and managing health issues.
Impact:
- Timely Interventions: Access to regular check-ups and screenings aids in early disease detection and intervention.
- Treatment Adherence: Adequate healthcare access ensures individuals can adhere to treatment plans, minimizing complications.
- Healthcare Disparities: Limited access contributes to health disparities, as marginalized populations often face barriers to receiving quality care.
Social Support Networks
Social support networks comprise the relationships, connections, and interactions that individuals have with family, friends, and community.
Significance:
Strong social support networks contribute to overall mental and physical well-being.
Impact:
- Emotional Well-being: Social support mitigates stress, depression, and anxiety, fostering better mental health.
- Health Behaviors: Peer influence can positively affect health behaviors, such as exercising or quitting smoking.
- Coping Mechanisms: Social networks provide outlets for sharing concerns, thus aiding in effective coping during challenges.
Education and Literacy
Education and literacy refer to an individual’s level of formal education and ability to comprehend and apply health-related information.
Significance:
Education is a key determinant that influences health knowledge and decision-making.
Impact:
- Informed Choices: Higher education levels lead to a better understanding of health information, enabling informed decision-making.
- Preventive Actions: Health literacy empowers individuals to engage in preventive measures and seek appropriate medical care.
- Adherence to Medical Instructions: Educated individuals are more likely to understand and follow medical instructions accurately.
Intersections and Implications
The five social determinants of health are interconnected and often intersect across various axes, such as race, ethnicity, gender, and age. This intersectionality further exacerbates health disparities, as individuals facing multiple disadvantages may experience compounded challenges.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health
To promote health equity and address health disparities stemming from these determinants, strategies encompassing policy changes, community engagement, healthcare access improvement, education, and cross-sector collaboration are vital.
Summary: What are the Five Social Determinants of Health
Recognizing the multifaceted nature of health requires an understanding of the five key social determinants of health. These determinants interact in complex ways, creating a tapestry of influences on health outcomes. By addressing these determinants systematically, societies can work towards creating a more equitable and healthier environment where everyone has the opportunity to achieve their best possible health and well-being.
Related Articles:
Follow us: What are the Five Social Determinants of Health