Definition-
SHOCK- Types, Etiology and Pathophysiology
Shock is a life-threatening clinical syndrome of cardiovascular collapse characterized by:
- An acute reduction of effective circulating blood volume (hypotension).
- Inadequate perfusion of cells and tissues (hypoperfusion).
In other words, it may be defined as inadequate delivery of oxygen and nutrients to maintain normal tissue and cellular function.
TYPES OF SHOCK:
Primary or Initial Shock –
It is a transient and usually benign vasovagal attack due to the sudden reduction of venous return to the heart caused by neurogenic vasodilatation and consequent peripheral pooling of blood.
Causes:
- Trauma.
- Severe pain
- Emotional overreaction like fear.
Clinical Features: SHOCK- Types, Etiology and Pathophysiology
- Anxiety, restlessness, altered mental state.
- Hypotension.
- Rapid, weak pulse.
- Pale & clammy skin.
- Rapid and shallow respirations.
- Hypothermia.
- Unconsciousness.
Secondary or True shock-SHOCK- Types, Etiology and Pathophysiology
It is a circulatory imbalance between oxygen supply and oxygen requirements at the cellular level therefore also known as Circulatory Shock.
CLASSIFICATION OF SHOCK: SHOCK- Types, Etiology and Pathophysiology
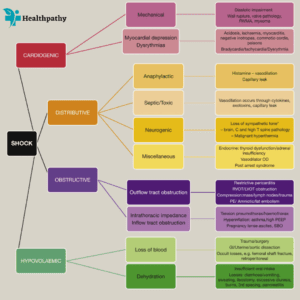
ETIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:

PATHOGENESIS:
Generally, all the forms of shock involve following derangements:
1. Reduce effective circulatory blood volume: It may result from-
- By actual loss of blood volume.
- By decreased cardiac output without actual loss of blood.
2. Impaired tissue oxygenation: Decreased effective circulatory blood volume causes reduced oxygen supply to the tissues and organs resulting in the tissue anoxia and further cellular injury.
3. Release of Inflammatory Mediators: In response to the cellular injury, innate immunity of the body gets activated and release inflammatory mediators which eventually becomes the cause of cell injury.
STAGES OF SHOCK:
Although deterioration of circulation in shock is a progressive & continuous phenomenon & compensatory mechanisms become progressively less effective. The stages are:-
1. Non – progressive (initial. Compensated reversible)shock.
2. Progressive decompensated shock.
3. Decompensated (irreversible) shock.
More to read:


Follow us:





